14-4: New Directions in Leadership Research
 Leadership Development Programs
Leadership Development Programs
Leadership development programs should address multiple competencies including technical skills, interpersonal capabilities, emotional intelligence, and strategic thinking. Effective development requires assessment of current capabilities, identification of development needs, and provision of appropriate learning experiences.
The Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology (SIOP) identifies leadership development and coaching as one of the top work trends shaping the future of organizations. Leadership coaching is no longer reserved for executives – SIOP highlights the growing use of coaching at all levels to support leadership development, especially in hybrid and remote environments.
360-Degree Feedback
360-degree feedback provides comprehensive assessment by gathering evaluations from supervisors, peers, subordinates, and customers. This multi-source feedback enables leaders to understand how their behavior affects different stakeholders while identifying improvement opportunities.
Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching and mentoring relationships provide personalized development support through experienced leaders who can share knowledge, provide guidance, and offer feedback. These relationships often prove more effective than formal training programs for developing leadership capabilities. Coaching helps leaders reflect on their behaviors, align with organizational values, and build stronger relationships with their teams.
Leadership Ethics and Responsibility
Ethical Leadership
Ethical leadership involves demonstrating high moral standards while influencing others to behave ethically. Ethical leaders serve as role models who establish clear ethical expectations while creating climates that support ethical decision-making.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility expectations require leaders to consider organizational impacts on society and environment while pursuing business objectives. This broader perspective requires balancing multiple stakeholder interests rather than focusing solely on shareholder returns.
Virtual and Distributed Leadership
Virtual Leadership
Virtual leadership challenges traditional leadership approaches by requiring influence without face-to-face interaction. Virtual leaders must develop new competencies for building relationships, communicating effectively, and coordinating activities across distances and time zones.
With the rise of hybrid work, SIOP recommends that leaders develop new competencies in digital communication, remote collaboration, and outcome-based performance management. Effective hybrid leaders balance flexibility with accountability and ensure that all team members feel connected and supported.
Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership involves sharing leadership responsibilities across multiple individuals rather than concentrating authority in single leaders. This approach can enhance organizational agility while developing leadership capabilities throughout organizations.
Future Directions in Leadership Research
Emerging Leadership Challenges
Emerging leadership challenges include managing diverse and distributed workforces, integrating artificial intelligence and automation, addressing sustainability concerns, and navigating rapid organizational change.
Complexity Leadership
Complexity leadership approaches recognize that contemporary organizations operate in complex adaptive systems requiring different leadership approaches than traditional hierarchical models.
Authentic Leadership
Authentic leadership focuses on self-awareness, relational transparency, balanced processing, and moral perspective as foundations for leadership effectiveness.
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership emphasizes leaders’ responsibility to serve followers and broader communities rather than pursuing personal power or success.
Practical Applications and Recommendations
Leadership Selection
Leadership selection should employ multiple assessment methods including personality assessment, cognitive ability testing, situational judgment tests, and behavioral interviews. Effective selection requires clear leadership competency models while considering situational requirements and organizational culture.
Leadership Development Programs
Leadership development programs should combine multiple learning approaches including formal training, experiential learning, coaching, mentoring, and stretch assignments.
Organizational Culture
Organizational culture must support effective leadership through policies, practices, and norms that reinforce desired leadership behaviors.
SIOP Insights on Contemporary Leadership
The Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology (SIOP) identifies leadership development and coaching as one of the top work trends shaping the future of organizations. As workplaces become more complex, diverse, and hybrid, leadership effectiveness increasingly depends on adaptability, emotional intelligence, and inclusive practices.
Key Themes from SIOP Research
- Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
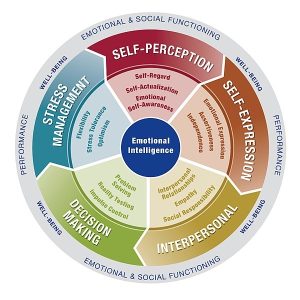
Key components of emotional and social functioning, including self-perception, self-expression, interpersonal skills, decision-making, and stress management. These dimensions contribute to overall well-being and performance in personal and professional contexts.
SIOP emphasizes that emotionally intelligent leaders are better equipped to navigate uncertainty, foster psychological safety, and build trust across diverse teams. Leaders who demonstrate empathy, self-awareness, and emotional regulation are more effective in motivating others and managing conflict.
- Coaching and Development
Leadership coaching is no longer reserved for executives. SIOP highlights the growing use of coaching at all levels to support leadership development, especially in hybrid and remote environments. Coaching helps leaders reflect on their behaviors, align with organizational values, and build stronger relationships with their teams.
- Inclusive Leadership
SIOP research underscores the importance of inclusive leadership – leaders who actively seek out diverse perspectives, create equitable opportunities, and foster belonging. Inclusive leaders are associated with higher team engagement, innovation, and retention.
- Leading Hybrid Teams
With the rise of hybrid work, SIOP recommends that leaders develop new competencies in digital communication, remote collaboration, and outcome-based performance management. Effective hybrid leaders balance flexibility with accountability and ensure that all team members feel connected and supported.
Practical Recommendations
- Integrate emotional intelligence training into leadership development programs
- Provide access to coaching and mentoring for emerging leaders
- Evaluate leaders not just on results, but on how they lead – especially in terms of inclusion and well-being
- Equip leaders with tools and strategies for managing distributed teams
By embracing these evidence-based practices, organizations can cultivate leadership that is not only effective but also human-centered, resilient, and future-ready.
Conclusion
Leadership theory has evolved dramatically from early trait approaches to contemporary recognition of leadership as complex, contextual, and relational phenomena. This evolution reflects our growing understanding that leadership effectiveness depends on sophisticated interactions between multiple factors rather than simple formulas or universal prescriptions.
The movement from seeking universal leadership solutions to recognizing contingency approaches highlights the complexity leaders face in real organizational settings. Effective leadership requires understanding not just what to do, but when and how to adapt approaches based on followers, situations, and organizational contexts.
Contemporary emphasis on transformational leadership, emotional intelligence, and relationship quality highlights the fundamentally interpersonal nature of leadership while recognizing its role in organizational change and adaptation. These perspectives suggest that leadership development must address both technical competencies and interpersonal capabilities.
Cultural and gender considerations reflect increasing organizational diversity while highlighting the need for inclusive leadership approaches that value different perspectives and styles. Global organizations must develop culturally sensitive leadership approaches while maintaining organizational coherence.
Future leadership challenges will likely require continued theory development as organizations face unprecedented complexity, uncertainty, and change. Leaders must develop new competencies while maintaining fundamental capabilities for influence, inspiration, and results achievement.
For you as a future leader – whether you’re aspiring to formal leadership positions or simply wanting to be more effective in influencing others toward positive goals – the key takeaway is that leadership is both learnable and adaptable. Understanding these theories and research findings gives you a foundation for developing your own leadership approach while remaining flexible enough to adapt to different situations, followers, and organizational contexts.
Success in leadership ultimately depends on integrating knowledge, skills, and personal qualities that enable effective influence relationships while achieving meaningful results for individuals, groups, and organizations. This integration requires both scientific understanding and practical wisdom that develop through experience, reflection, and continuous learning.
Media Attributions
- Leadership © Nick Youngson is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
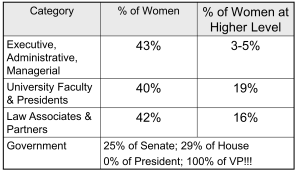
- Leadership Glass Ceiling??
- Emotional Intelligence © F.derakhshan is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
