Module 08: Sleep

Description: This module examines consciousness, circadian rhythms, sleep stages, & dreaming from a neuroscience perspective. Students will explore biological rhythms & the suprachiasmatic nucleus, analyze EEG patterns across wakefulness & sleep stages, examine brain mechanisms controlling sleep & REM, & evaluate theories of sleep function & dreaming. The module covers sleep disorders including insomnia, sleep apnea, narcolepsy, & parasomnias.

Why This Module is Important: Understanding sleep neuroscience is essential for counseling, clinical practice, & health psychology, providing biological foundations for addressing sleep disorders & understanding consciousness.
For counselors, this module provides:
- Understanding of sleep architecture & circadian rhythms for addressing client sleep complaints.
- Knowledge of sleep disorders & their neurological basis for appropriate referrals.
- Insight into how sleep deprivation affects mood & cognition relevant to mental health.
- Framework for understanding dream theories & their therapeutic implications.
For other psychology professionals, this module supports:
- Research into sleep’s role in memory consolidation & learning.
- Clinical assessment of sleep disorders & their psychological impacts.
- Educational approaches recognizing sleep’s importance for cognitive development.
- Understanding of consciousness & altered states from neuroscience perspective.
Module Learning Objectives: By the end of this module students will be able to…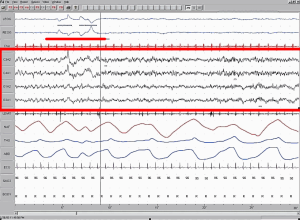
- MLO1: Identify circadian rhythm mechanisms, sleep stages & their EEG characteristics, & brain structures controlling sleep & wakefulness. (CLO1, ULO3)
- MLO2: Analyze biological rhythms including the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, compare SWS & REM sleep patterns, & evaluate neurochemical systems regulating sleep-wake cycles. (CLO2, CLO3, ULO3)
- MLO3: Evaluate theories of sleep function & dreaming (physiological versus psychological explanations), & assess treatment approaches for sleep disorders. (CLO2, CLO4, ULO3)
Test Yourself: If you truly “know” this material then you will be able to…
- Describe the suprachiasmatic nucleus as master biological clock, identify zeitgebers, distinguish sleep stages by EEG patterns (alpha/beta in waking, theta in Stages 1-2, delta in Stages 3-4, desynchronized in REM), & identify brain structures controlling sleep (basal forebrain, reticular formation, locus coeruleus, raphe nuclei). (MLO1)
- Explain circadian rhythms on 25-hour cycles, analyze why phase advances are harder than phase delays, compare brain activity across wakefulness/SWS/REM, describe PGO waves, & evaluate neurochemical contributions including norepinephrine & serotonin. (MLO2)
- Compare dream theories (Freud’s wish fulfillment, cognitive information-processing, activation-synthesis), evaluate sleep functions (protection, restoration, memory consolidation), & distinguish sleep disorders including insomnia, sleep apnea, narcolepsy, & parasomnias. (MLO3)
Media Attributions
- Sleeping Buddy © Microsoft Copilot adapted by Jay C. Brown is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- The Shepherd’s Dream © Johann Heinrich Füssli
- Sleep EEG REM © MrSandman is licensed under a Public Domain license
