Module 13: Sex & Love

Description: This module explores the neuroscience of sexual behavior, attraction, & parenting. Students will examine how hormones influence sexual development, orientation, & behavior, & how brain structures & genetics contribute to gender identity & romantic attachment. Topics include the sexual response cycle, sexually dimorphic brain structures, hormonal regulation, & the neurobiology of love & bonding.

Why This Module is Important: Understanding the biological basis of sex & love is essential for psychology professionals working in clinical, counseling, developmental, & health contexts. This module provides insight into how biology interacts with culture, identity, & emotion.
For counselors, this module provides:
- A framework for discussing gender identity, sexual orientation, & romantic relationships.
- Understanding of how hormonal & neurological factors influence behavior & emotional connection.
- Tools for addressing sexual dysfunction & relationship dynamics in therapy.
For other psychology professionals, this module supports:
- Research into sexual development, orientation, & bonding.
- Educational strategies for teaching about gender & sexuality.
- Clinical assessment of sexual health & identity-related concerns.
- Integration of neuroscience into developmental & social psychology.
Module Learning Objectives: By the end of this module students will be able to…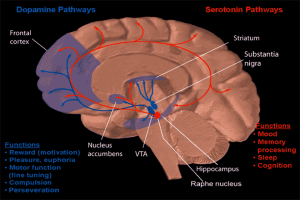
- MLO1: Describe the hormonal & neural mechanisms underlying sexual behavior & reproductive cycles. (CLO1, ULO3)
- MLO2: Analyze the biological & neurological correlates of sexual orientation, gender identity, & romantic attachment. (CLO2, CLO3, ULO3)
- MLO3: Evaluate ethical, cultural, & political implications of neuroscience research on sex, gender, & love. (CLO3, CLO4, ULO3)
Test Yourself: If you truly “know” this material then you will be able to…
- Explain how hormones like testosterone, estrogen, oxytocin, & vasopressin influence sexual behavior & parental bonding. (MLO1)
- Analyze how brain structures such as INAH-3 & SDN-POA relate to sexual orientation & gender differences. (MLO2)
- Evaluate how neuroscience findings have been used—and misused—in debates about gender identity & sexual orientation. (MLO3)
Media Attributions
- Lovin’ Buddy © Microsoft Copilot adapted by Jay C. Brown is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Cupid and Psyche © François-Édouard Picot is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Dopamine & Serotonin Pathways © NIH is licensed under a Public Domain license
