Module 09: Learning & Memory

Description: This module examines neural mechanisms underlying learning & memory. Students will explore nonassociative learning (habituation, sensitization) & associative learning (classical conditioning) using invertebrate & vertebrate models. The module covers memory systems including sensory, short-term, & long-term memory, the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation, & long-term potentiation as a mechanism for synaptic plasticity.

Why This Module is Important: Understanding learning & memory neuroscience is essential for counseling, educational, & clinical practice, providing biological foundations for understanding memory disorders & optimizing learning interventions.
For counselors, this module provides:
- Understanding of how trauma memories form & consolidate for PTSD treatment approaches.
- Knowledge of memory systems relevant to client recall & therapeutic memory work.
- Insight into neural plasticity supporting learning in therapy & behavior change.
- Framework for understanding memory reconsolidation in treating anxiety & trauma.
For other psychology professionals, this module supports:
- Research into memory formation, consolidation, & retrieval mechanisms.
- Educational strategies based on understanding of neural learning processes.
- Clinical assessment of memory disorders & amnesias.
- Understanding of how experiences physically change brain structure through synaptic plasticity.
Module Learning Objectives: By the end of this module students will be able to…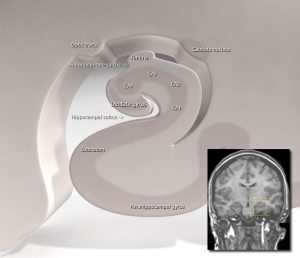
- MLO1: Identify types of learning (habituation, sensitization, classical conditioning) & memory systems (sensory, short-term, long-term), & describe neural structures involved including the hippocampus & amygdala. (CLO1, ULO4)
- MLO2: Analyze mechanisms of learning at the synaptic level using Aplysia models, evaluate the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation, & explain long-term potentiation as a basis for synaptic plasticity. (CLO2, CLO3, ULO4)
- MLO3: Evaluate evidence from patient H.M. & other case studies distinguishing explicit from implicit memory, & critically assess applications including memory reconsolidation for PTSD treatment. (CLO2, CLO4, ULO4)
Test Yourself: If you truly “know” this material then you will be able to…
- Distinguish nonassociative learning (habituation, sensitization) from associative learning (classical conditioning with CS, US, CR, UR), describe Kandel’s synaptic changes in Aplysia, & identify the hippocampus for memory consolidation & amygdala for emotional learning. (MLO1)
- Explain synaptic mechanisms in habituation (decreased neurotransmitter) versus sensitization (increased release), analyze the lateral interpositus nucleus role in eyeblink conditioning, describe hippocampal encoding before cortical consolidation, & explain long-term potentiation as increased synaptic efficiency. (MLO2)
- Evaluate patient H.M.’s anterograde amnesia following temporal lobe removal, distinguish his intact short-term & procedural memory from impaired explicit memory, & critically examine memory reconsolidation for PTSD treatment versus memory erasure. (MLO3)
Media Attributions
- Learning Buddy © Microsoft Copilot is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- St. Augustine in his Study © Sandro Botticelli is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Hippocampus © Frank Gaillard is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
