Module 04: Neurons

Description: This module explores neurons & glial cells as fundamental building blocks of the nervous system. Students will examine neuronal structure including cell membrane, organelles, axons, & dendrites, & understand mechanisms of electrical signaling including resting potential, action potentials, & propagation. Students will also learn about critical roles of glial cells in supporting neural function.

Why This Module is Important: Understanding neurons & neural communication is foundational for psychology & neuroscience, particularly for counselors, clinicians, educators, & researchers who need to understand how brain processes information & how cellular dysfunction manifests in psychological symptoms.
For counselors, this module provides:
- Biological framework for understanding how medications work at the cellular level.
- Insight into how neurological conditions (like multiple sclerosis) impact behavior.
- Understanding of how neurotoxins & substances disrupt neural transmission for substance abuse counseling.
- Knowledge of neural plasticity supporting recovery & therapeutic interventions.
For other psychology professionals, this module supports:
- Research into cellular-level disruptions contributing to psychological disorders.
- Development of targeted interventions based on neural mechanisms.
- Educational approaches recognizing how learning changes neural structures.
- Critical evaluation of neuroscience claims in media & literature.
Module Learning Objectives: By the end of this module students will be able to…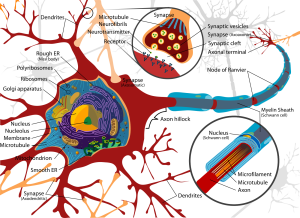
- MLO1: Identify the structural components of neurons & glial cells, including organelles, membrane structures, & cytoskeletal elements. (CLO1, ULO4)
- MLO2: Analyze the mechanisms of electrical signaling in neurons, including ion channels, pumps, & membrane potential in generating & propagating action potentials. (CLO2, CLO3, ULO4)
- MLO3: Evaluate the significance of glial cells in neural function & assess implications of research challenging traditional views of glia. (CLO2, CLO4, ULO4)
Test Yourself: If you truly “know” this material then you will be able to…
- Describe structure & function of neuronal components (cell body, dendrites, axons, myelin, axon hillock, synaptic vesicles) & explain how structural variations relate to functional differences (unipolar, bipolar, multipolar; sensory, motor, interneurons). (MLO1)
- Explain how resting potential is maintained through ion distribution & membrane permeability, trace action potential events (depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization), & compare passive versus saltatory conduction in speed & energy efficiency. (MLO2)
- Evaluate evidence for expanded glial cell roles (astrocytes in synaptic regulation, oligodendrocytes in signal speed, microglia in neuroplasticity) & discuss implications for understanding neural communication & treating neurological conditions. (MLO3)
Media Attributions
- Neuron Buddy © Microsoft Copilot adapted by Jay C. Brown is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Starry Night © Vincent van Gogh is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Complete Neuron Cell Diagram © LadyofHats is licensed under a Public Domain license
