Unit 1: Building Blocks of Neuroscience
Description: This unit establishes fundamental building blocks of neuroscience, progressing from broad conceptual foundations to molecular mechanisms of neural communication. Beginning with neuroscience history, methods, & ethics, we explore nervous system organization, genetic & developmental processes, neuronal structure & electrical signaling, & finally synaptic transmission & neurotransmitter function. These five modules create a comprehensive foundation for understanding how the brain enables psychological processes.

Why This Unit Is Important: Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for psychological practice & research, forming the scientific foundation for understanding how biological processes underlie behavior & preparing you to critically evaluate neuroscience claims.
For counselors, this unit provides:
- Scientific literacy to understand psychopharmacological interventions & communicate with medical professionals.
- Framework for recognizing when symptoms have neurological origins, supporting appropriate referrals.
- Understanding of how substances & medications affect the brain for counseling & medication discussions.
- Knowledge of developmental neuroscience informing trauma-informed care & critical periods.
- Ethical grounding for working with vulnerable populations.
For other psychology professionals, this unit supports:
- Research design & methodology for studying brain-behavior relationships.
- Educational practice recognizing biological basis of learning & memory.
- Clinical assessment integrating neurobiological understanding with psychological symptoms.
- Evidence-based practice drawing on neuroscience research.
- Professional communication with interdisciplinary teams.
Unit Learning Objectives: By the end of this unit students will be able to…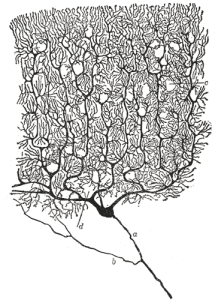
- ULO1: Define neuroscience as a discipline & identify its major subdisciplines, historical developments, research methodologies, & ethical principles. (CLO1, CLO2, CLO3)
- ULO2: Identify major divisions & organization of the nervous system, including anatomical terminology, structural components, protective mechanisms, & evolutionary principles. (CLO1, CLO4)
- ULO3: Explain how genetic mechanisms & developmental processes influence neural structure & function across the lifespan, including gene expression & gene-environment interactions. (CLO1, CLO2)
- ULO4: Describe structural & functional characteristics of neurons & glial cells, including cellular components, membrane properties, & mechanisms of electrical signaling. (CLO1, CLO2)
- ULO5: Analyze synaptic transmission & neurotransmitter function, & evaluate how neurotransmitter systems relate to psychological functions & clinical interventions. (CLO2, CLO3, CLO4)
Media Attributions
- Building Buddy © Microsoft Copilot adapted by Jay C. Brown is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- The Lacemaker © Jan Vermeer is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Drawing of Neurons © Santiago Ramon y Cajal is licensed under a Public Domain license
