Module 11: Observational Learning 1
Module 11: Observational Learning 1
 Description: If all we had to work with was classical & operant conditioning, we would not be able to learn all that many adaptive skills since these require direct experience. Once we add the ability to watch others, or even better listen to them or read what they wrote, we can greatly increase the number of adaptive behaviors we can learn.
Description: If all we had to work with was classical & operant conditioning, we would not be able to learn all that many adaptive skills since these require direct experience. Once we add the ability to watch others, or even better listen to them or read what they wrote, we can greatly increase the number of adaptive behaviors we can learn.
Why This Module Is Important: Understanding observational learning mechanisms explains how humans acquire complex behaviors efficiently:

- Behavioral Therapy: Foundation for modeling techniques in Module 13; understand how clients learn maladaptive behaviors from models; design interventions using appropriate models
- Child Development: Explain how children acquire language, social skills, & emotional regulation through observation; understand autism as observational learning deficit
- Skill Training: Apply Bandura’s four processes (attention, retention, motor reproduction, motivation) to optimize training effectiveness in education, sports, & workplace settings
- Cultural Understanding: Recognize observational learning as the mechanism for cultural transmission; understand how behaviors spread through populations without direct reinforcement
- Neural Mechanisms: Mirror neuron research explains empathy, theory of mind, & why observational learning is uniquely powerful in humans
Observational learning extends beyond operant conditioning by allowing behavior change without direct experience of consequences.
Module Learning Objectives: By the end of this module students will be able to…
- MLO1: Distinguish between social facilitation, local enhancement, imitation, & true social learning. (CLO1, ULO1)
- MLO2: Evaluate the role of mirror neurons in observational learning & theory of mind. (CLO2, ULO1)
- MLO3: Explain Bandura’s social-cognitive theory including the four processes required for observational learning. (CLO3, ULO1)
Test Yourself: If you truly “know” this material then you will be able to…
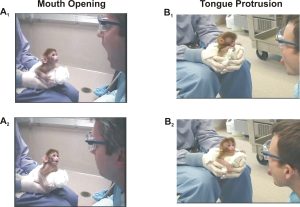
- Classify examples of animal behavior (octopus opening jars, rats learning food preferences, deer running from predators) as social facilitation, local enhancement, or true social learning based on cognitive demands. (MLO1)
- Analyze how mirror neuron deficits in autism spectrum disorder explain difficulties with imitation, empathy, & theory of mind tasks. (MLO2)
- Apply Bandura’s four processes (attention, retention, motor reproduction, motivation) to diagnose why a corporate training video failed to change employee behavior. (MLO3)
Media Attributions
- Professor Learnwell © Microsoft Copilot adapted by Jay Brown is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- The Music Contest © Jean-Honoré Fragonard is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Neonatal Imitation in Rhesus Macaques © P.F. Ferrari et. al. is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
